What is Difference Between Tracheids And Vessels?
Difference Between Tracheids And Vessels is that Tracheids and vessels are two types of conductive elements that are found in the xylem of plants. Both tracheids and vessels are involved in providing mechanical support to the plant as well. Both conductive elements consist of tubular structures.
tracheids are narrow and less efficient in water conduction, while vessels are wide and highly efficient in water conduction. Tracheids are the main 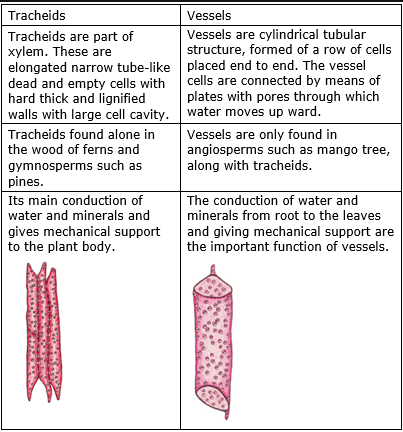 conductive elements of ferns and gymnosperms. In contrast, the vessels are the main conductive elements in angiosperms. The other two cellular components of the xylem are the xylem fibers and the xylem parenchyma.
conductive elements of ferns and gymnosperms. In contrast, the vessels are the main conductive elements in angiosperms. The other two cellular components of the xylem are the xylem fibers and the xylem parenchyma.
What are tracheids?
Tracheids are one of the two conductive elements in the xylem of angiosperms. Tracheids are also present in ferns and gymnosperms as their main conductive elements. Angiosperms have both vessels and tracheids; therefore, tracheids are only elements of secondary conduction in angiosperms.
Tracheids consist of a single cell with pointed ends. The diameter of the tracheids is about 30 μm. During the thickening of the secondary cell wall, the tracheids are highly lignified, forming a polygonal cross-section. Only the regions of the pools are not lignified. After lignification, the tracheids become dead cells. Your protoplast empties with maturation. In addition to water conduction, tracheids are capable of providing mechanical resistance to plants. They provide mechanical resistance to softwood plants. Due to the high surface-volume ratio, tracheids can hold water against gravity.
What are the ships?
Vessels are the other type of conductive elements found only in angiosperms. The vessels do not contain a protoplasm at maturity, and the thickening of the secondary cell wall by lignification produces a dead tubular cell for water conduction. These lignified vessels are also involved in providing mechanical resistance to plants. Wood consists mainly of grasses.
The vessels are shorter cells with a lumen wider than the tracheids. Due to the increase in diameter, the vessels conduct water more efficiently than the tracheids. In addition, the vessels are arranged end to end, forming a tube. The ends of the vessels are made up of perforation plates. Some drilling plates consist of a single opening. Some may consist of several elongated openings. Another type of perforation plates may consist of several round openings or net-shaped openings. The presence of a drilling plate increases the water conduction efficiency. The elements of the oak vase are shown in Figure 2.
Similarities between tracheids and vessels
- Tracheids and vessels are two components of the xylem.
- Both tracheids and vessels are tubular cells.
- Both tracheids and vessels are dead at maturity since they have secondary lignification.
- Both tracheids and vessels are found in both the primary and secondary xylem.
- Both tracheids and vessels participate in the conduction of water along the stem and also provide mechanical support to the plant.
Differences
Definition
Tracheids: Tracheids are tubular cells in the xylem of vascular plants, which participate in the conduction of water from the roots to the leaves.
Vessels: The vessels are elongated dead cells found in the xylem of flowering plants, formed by perforated cell walls through which water flows.
Found in
Tracheids: Tracheids are present in all vascular plants.
Vessels: Vessels are only present in angiosperms.
Origin
Tracheids: Tracheids originate from a single cell.
Vessels: The vessels originate from a longitudinal archive of cells. Therefore, they produce continuous tubes.
Light diameter
Tracheids: Tracheids contain a narrow lumen.
Glasses: The glasses contain a wide lumen.
Wells
Tracheids: Tracheids consist of a smaller number of large wells.
Vessels: Ships contain a large number of small wells.
Perforated / Imperforated Cells
Tracheids: Tracheids are imperforated cells.
Vessels: The vessels are perforated cells.
Water Conduction Efficiency.
Tracheids: Tracheids are inefficient in water conduction since they are cells without perforations.
Glasses: Ships are efficient in water conduction.
Cell wall thickness
Tracheids: Tracheids contain thin cell walls.
Vessels: The vessels contain highly thickened cell walls.
Cross-section
Tracheids: Tracheids contain polygonal cross-sections.
Vessels: Ships contain circular cross sections.
Average length
Tracheids: Tracheids are shorter cells (approximately 1 mm long).
Vessels: The vessels are longer cells (about 10 cm long).
End
Tracheids: Tracheids contain conical end walls.
Vessels: The vessels contain diagonal or transverse sidewalls.
End to end connection
Tracheids: Tracheids are connected laterally.
Vessels: Ships are connected from end to end.
Surface / volume ratio
Tracheids: Tracheids consist of a high surface/volume ratio.
Glasses: The containers consist of a low surface/volume ratio.
Air embolism prevention
Tracheids: Tracheids prevent air embolism due to their high adhesion strength in the narrow tube.
Vessels: Ships do not prevent air embolism.
conclusion
Tracheids and vessels are the two conductive elements of water found in the xylem. Tracheids are the main conductive element of ferns and gymnosperms. The vessels are only present in the angiosperms. The diameter of the tracheids is smaller than that of the vessels. In addition, the vessels consist of perforation plates at the ends of the cells. Therefore, the efficiency of water conduction is high in the vessels than in the tracheids. Both tracheids and vessels participate in the supply of mechanical resistance to plants. The main difference between tracheids and vessels is their diameter and the efficiency in water conduction.
You May Also Interested:
