Neurotransmitters: functions and types
Types of Neurotransmitters: Thanks to the functioning of our nervous system, we can be aware of our internal and external world, we understand and give meaning to everything that happens to us, what we see, we can learn and carry out what we learn effectively. The nervous system is responsible for coordinating and integrating all the activities of the different systems of our body. When we talk about neurotransmitters, we refer to those chemical substances generated by the body that are responsible for emitting signals (information) from one neuron to another through a process called synapse. 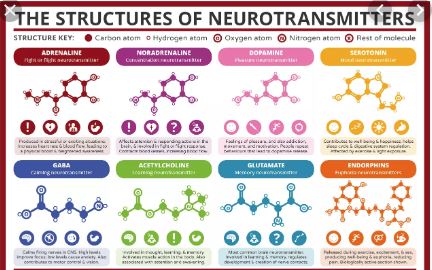
The neurotransmitter is released through the vesicles through a nerve impulse, then goes through what is called the presynaptic space to finally interact with the postsynaptic neuron modifying its action potential, producing a determined physiological response.
What are neurotransmitters and their functions
Neurotransmitters are biomolecules that are responsible for transmitting information from one neuron to another that are linked by a synapse (intercellular junction that is responsible for the transmission of information between one cell and another by electrical impulses), in which the neuron Presynaptic is responsible for issuing information and the postsynaptic neuron is responsible for receiving it.
The main function of neurotransmitters is to inhibit or excite the activity of the postsynaptic cell, that is, depending on the type of receptor, neurotransmitters can enhance or decrease their functioning. It is important to mention that the effect that neurotransmitters exert on neurons can be short term (for a few seconds) or long term (for months and even years).
Research on neurotransmitters is extremely important because thanks to them we can learn more about several of the higher cognitive processes in which they are involved, such as memory, thinking, attention, language, learning, etc.
Types of neurotransmitters
1. Dopamine
Dopamine is one of the most popular types of neurotransmitters, and it is directly related to the feeling of well – being, pleasure and relaxation. Dopamine originates in an area of the brain that is known as a black substance and fulfills a very important function in the control of our musculoskeletal system, so it coordinates movement.
Being also essential for the proper functioning of the central nervous system, it performs a role that is key in human behavior, which is why it is called the neurotransmitter of happiness.
Another important function with which this type of neurotransmitter fulfills is that by producing a depolarizing effect in neurons, there is excellent communication between them, which favors learning, attention, and memory.
2. Serotonin
This type of neurotransmitter also serves as a hormone. It is located in different sections of the central nervous system and its main function is to regulate the activity of other neurotransmitters.
Serotonin is directly involved in various processes such as digestion, regulation of anxiety and stress levels, body thermal regulation, sleep, appetite, mood, and sexual desire.
3. Noradrenaline
This type of neurotransmitter is also known as the stress hormone and, like serotonin, it serves a double function (neurotransmitter and hormone). Norepinephrine is responsible for activating the sympathetic nervous system and is associated with heart rate and certain processes responsible for attention and the generation of a stress response.
4. Adrenaline
This neurotransmitter that is extremely similar to norepinephrine, is responsible for developing survival mechanisms when we are in real or even imaginary danger. It also meets some physiological reactions, such as breathing and blood pressure.
5. Glutamate
It is the main excitatory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system. Glutamate is related to the GABA neurotransmitter and has a very important role in memory processes and their recovery, among other mental processes.
6. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
This type of neurotransmitter is responsible for stopping or inhibiting the action of some excitatory neurotransmitters. The goal of doing so is to prevent us from having certain reactions of exaggerated fear and anxiety and that only causes us discomfort.
7. Acetylcholine
This neurotransmitter is found in different areas of the central nervous system, at synapses of glands and in muscles. It is responsible for stimulating muscles, activating motor neurons, promotes memory and association processes, as well as the transition from sleep to wakefulness.
Classification of neurotransmitters
The classification of neurotransmitters is as follows:
- Amino acids: these are organic compounds that represent a large number of functions of the body and combine to form proteins. They are basically responsible for maintaining energy and oxygen, which is why they are considered essential for metabolism processing.
- Purines: they are chemical compounds that are mainly responsible for transporting information acting as chemical messengers.
- Gases: it is one of the most important chemical compounds since it performs multiple functions, such as the largest vasodilator compound in the whole organism.
- Peptides: they are distributed throughout the membrane that covers the brain and is responsible for issuing an outward response.
- Esters: within this group of neurotransmitters, is acetylcholine, which is an excitatory type neurotransmitter and, sometimes, can perform some inhibitory function.
You May Also Like:
