What is Difference Between Sex and Gender?
Difference Between Sex and gender is that Sex refers to the set of characteristics physical and biological defined genetically determining whether a living being is male, female, or intersexual. Sex chromosomes and phenotypic factors are key factors in the assignment of a human’s sex.
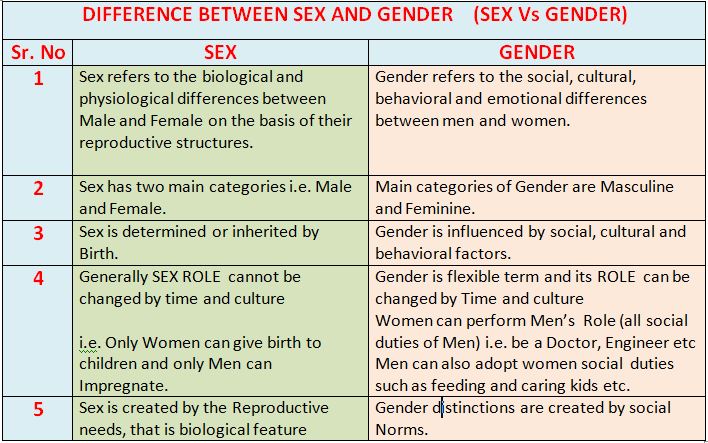
The genre covers a number of roles, behaviors, and attributes socially constructed that are considered appropriate for a person according to their biological sex. These social constructions are traditionally linked to the categories of men and women, but little by little many other gender identities have been recognized. The social, cultural and space-time contexts are decisive in the definition of gender.
| Definition | Sex Physical and biological characteristics that define the sex of a living being. |
Gender It refers to the set of characteristics, behaviors, and roles attributed to a person because of their biological sex that is considered socially appropriate. |
| Features |
|
|
| Categories | Male, female, and, to a lesser extent, intersexual. | Man, woman, cisgender, transgender, among others. |
What is sex?
Sex refers to the set of particular physical and biological attributes that define a male, a female or an intersexual. For example, in the case of humans, it belongs to one sex or another depending on factors such as genetic composition, hormonal processes and phenotypic characteristics.
When talking about phenotypic sexual characteristics, these are the internal and external sexual characteristics that are observable in a person. For example, genitals, hormonal processes, reproductive system, physical/body constitution, etc. These characteristics begin to develop near the seventh week of gestation of the organism.
Sex characteristics
- It refers to the physical and biological attributes of a living being.
- The sexual attributes of a living being are determined by the X and Y sex chromosomes.
- Sexual characteristics mainly define two types of sex: the male and the female.
- There may be unusual cases of intersex people.
- The sex remains stable.
Sex chromosomes
The sex chromosomes are responsible for determining the sex of a living being. In humans, these chromosomes are X and Y, found in pairs (XX or XY). Half of the chromosomes that a human being possesses come from each of the parents.
The female has XX chromosomes, while the male has XY chromosomes. Biological sex is determined at the time fertilization occurs. The father donates in the sperm either an X or a Y chromosome, while in the mother’s ovum there are only X chromosomes.
Sexual characteristics develop according to the type of chromosomes present.
In the case of intersex, due to some particular situation at the genetic level, the chromosomes do not follow the XX or XY pattern, presenting themselves in another way (XYY, XXY, etc.). This results in sexual characteristics being atypical. In addition, intersexuality can also occur due to variations in phenotypic patterns (formation of glands, genital organs, etc.).
The sex of a person, in this case, is not clearly defined at the time it is born. An intersexual can begin his life with characteristic features of one sex, and then develop features of another sex.
What is gender?
The gender is the social perception we have of a person about what is appropriate in relation to their biological sex, sexual orientation, and other aspects of their identity. This perception is determined by the social and cultural context , as well as by the biological and psychological characteristics of an individual.
A person may have a gender identity different from that assigned in their society. It can be assigned before birth, usually associated with the person’s sex.
The characteristics that determine what it is to be a man and a woman vary at a temporal level (time) and at a spatial level (from culture to culture or society). So gender is fundamentally a social construction (a social product based on social practices and rules that varies from society to society).
It is common for gender to be associated only in response to the biological difference between the sexes, from a binary perspective. That is, from the male / female dichotomy there is a tendency to assume that there are only two genders: men and women.
Gender characteristics
- It can be a form of self-identification, as well as social perception.
- It is a social construct.
- There is no single way to act or behave according to a specific gender.
- Gender identity and gender roles change according to the socio-cultural context and throughout history.
- The definition of what a genre tends to change.
- There is no single way to live the genre.
Gender identity
Gender identity refers to how well a person is identified as being of the same gender. This identification with a gender is related to a person’s personal experiences, education, and social relationships, according to the patterns established for each gender.
Identity is an element that covers both a social and an individual sphere. On the one hand, a person is socially identified as part of a group, due to its proximity to socially shared practices and habits, as well as by physical attributes.
On the other hand, identity also relates to how a person sees himself as part of a group. It is the way in which a person defines himself in relation to other people, according to his physical and psychological taxes.
EXAMPLES OF GENDER IDENTITIES
Today it is more common to talk about the existence of different ways of living the gender, different from the binary division man/woman. Here are some general ways in which a person can express their gender identity:
- Cisgender: This refers to those people whose gender identity matches the biological sex assigned at birth. In general, these people represent what is considered the norm in many societies, in terms of gender identity.
- Transgender: When a person’s gender identity does not match their assigned biological sex. You can also talk about a trans person. This term covers a broad spectrum of gender identities and ways of expressing it that defy the social norm.
Gender roles
Gender roles express the expected behaviors that a person supposedly should have based on their sex. These are associated with someone’s gender identity, under the assumption that both must be equal.
Characteristics of gender roles
- They are behaviors assigned according to the biological sex of a person.
- They follow social norms.
- Differentiated behaviors are ascribed to each gender.
- Formal and informal education has a weight in learning these roles.
- They can result in gender bias.
Gender roles and social norms
These roles obey social norms and behaviors that in society are considered appropriate for each gender. However, gender roles do not necessarily go hand in hand with a person’s gender or gender identity.
Gender roles are reflected in the rights, duties, tasks, and responsibilities that are socially assigned to a person. They express themselves in the role in the family, work, within a sentimental relationship, rights over resources, sexual behaviors, sexual reproduction, etc.
For example, traditionally, women with children were assigned their care and to take care of household chores. In contrast, the man was assigned the task of being the family provider. That is, the traditional role of women was to be a caregiver, while that of men was to be a provider.
This does not mean that a woman cannot have a provider role in a family, or that a man cannot perform care work. In fact, in reality, both women and men perform tasks and behave in such a way that there is no clear limit that establishes what one gender or another should do. That is, gender roles are social constructions that do not necessarily adhere to reality.
Another example is the attribution of colors to a gender according to the sex of the person. In the case of children, it is usual to associate the color blue with the masculine, so it is promoted that they wear that color in many cultures. As for girls, pink is used in the same way.
However, at the beginning of the 20th century, in the United States, it was common to go the contrary. That is, the color of the girls was blue and that of the boys was pink. Over time, there was an investment in this social construction. Thus, the choice of color and its assignment to a gender responds more to social practices and habits than to a biological issue.
Gender bias in Difference Between Sex and gender
A gender-based prejudice means that there is a differentiated attitude in dealing with a person based on their gender.
It involves a discriminatory act, as it takes as factors that have nothing to do with a person’s abilities, often limiting their opportunities.
For example, this type of prejudice is socially manifested in the type of jobs or professional careers that are associated with one gender or another.
Consider that women are not able to occupy positions of hierarchy in a company,
Consider that women are not able to occupy positions of hierarchy in a company, because they are supposed to be more temperamental than men (because it is a job that requires a cold mentality or few emotions). Or that a man should not comb his daughter’s hair, because it is a task that the mother should do.
Other ways in which gender bias is manifested is when it is thought to be normal, and even valued, for a man to seek and maintain sexual relations with several women. Qualifiers such as “gallant” or “conqueror” are normally used. While if a woman performs the same acts, she is seen in a negative and derogatory light.
In fact, this type of prejudice has placed women in a socially disadvantaged position at the historical level, with respect to men and what is associated with the masculine.
That women did not have spaces for participation and political representation in most democratic countries, until a few decades ago, is a result of this type of prejudice.
You May Also Interested:
