What is Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis?
Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis is that The endocytosis is the transport of particles and substances inside the cell, while the exocytosis is intracellular transporting material outward. Both processes are due to the need of the cell to maintain with its surroundings an exchange of materials for its survival.
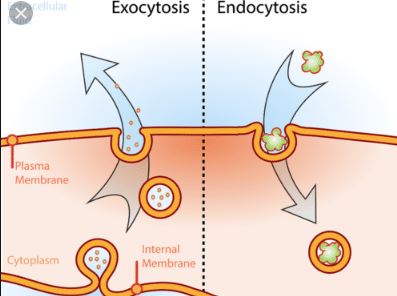
Both endocytosis and exocytosis are mechanisms involved in the transport of materials through the plasma membrane. This is a type of active mass transport that requires energy in the form of ATP.
Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis in Tabular Form
| Endocytosis | Exocytosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The cellular mechanism to trap substances from the extracellular environment. | The cellular mechanism to release or export content to the extracellular medium. |
| Process | The plasma membrane envelops and surrounds the substance. | Intracellular vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane. |
| Types | Phagocytosis (solid material) and pinocytosis (liquid material). | Constitutive secretory pathway and regulated secretory pathway. |
| Vesicle formation | Internal endocytic vesicles, called phagosomes, form | The secretory vesicles form in the Golgi apparatus. |
| Example | A white blood cell ingesting a bacterium. | Endocrine cells release hormones by exocytosis. |
What is endocytosis?
Endocytosis is the process by which cells capture material from the extracellular environment. In this process, the material to be ingested gradually closes in a small portion of the plasma membrane, which is introduced or invaded into the cell, to finally separate from the membrane and form an endocytic vesicle.
Cells use endocytosis to trap nutrients, such as vitamins, cholesterol, and iron. Depending on the size and consistency of the material to be ingested, there are two types of endocytosis: phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is the endocytosis of solid and large particles. Another way of looking at the phagocytosis process is like “the cell eating.” An example is unicellular organisms, such as amoebas, that use phagocytosis to feed.
In multicellular higher organisms, there are cells known as “professional phagocytes,” such as white blood cells or leukocytes and macrophages. These cells are responsible for defending the body against invading agents, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
The gallbladder resulting from phagocytosis is called phagosome. These phagosomes fuse with lysosomes, which are the intracellular organelles responsible for the digestion of the material.
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis is the internalization of dissolved molecules in a fluid. Pinocytosis can be translated as “the drinking cell”.
What is exocytosis?
Exocytosis is the cellular process to release material abroad. It is the reverse process of endocytosis. From the Golgi apparatus, vesicles are formed to fuse with the plasma membrane. There are two ways to execute secretion: constitutive and regulated.
Constitutive secretory route
In this way, the vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane continuously. This is the way the cell eliminates waste.
Regulated secretory pathway
To activate this pathway, some special signal is required within the cell that tells you that you must release the products within your secretory vesicles. This pathway is mainly found in cells specialized in secreting products, such as neurons, those release neurotransmitters, or endocrine cells that release hormones.
What is transcytosis?
In some cells, such as endothelial cells, the material is transported from one side of the cell to the other. This process is known as transcytosis.
At the cellular level, your body is a very busy place. Your cells create energy, secrete chemicals, expel waste and many, many other functions. Two key functions to which their cells are dedicated are exocytosis and endocytosis.
The definitions for exocytosis and endocytosis are as follows:
- Exocytosis – the process by which a cell expels molecules and other objects that are too large to pass through the cell membrane
- Endocytosis – the process by which a cell absorbs molecules and other objects that are too large to pass through the cell membrane
The basic mechanism in which a cell performs exocytosis or endocytosis is the same. Both make use of vesicles for molecular transport. Vesicles are small sacs covered by membranes that move around a cell. They are generally used for storage and transport because they are completely covered by a membrane, inside they can have a different composition than that of their cell.
How are vesicles used for exocytosis and endocytosis?
- Exocytosis – waste or other chemicals inside the cell are surrounded by the gallbladder. Sometimes the gallbladder is able to absorb the molecule through its membrane. Other times it surrounds the molecule and “swallows” it. Next, the gallbladder moves to the edge of the cell and adheres itself to the cell membrane.
- Endocytosis – The cell wraps molecules or proteins near the surface of the cell membrane. You can swallow large molecules, small pieces of protein, or create receptor bags that attract certain specific types of molecules. Once the molecule is surrounded by the cell membrane, the area is pinched to create a vesicle inside the cell that contains the molecule.
You could say that endocytosis creates vesicles and exocytosis uses and can potentially destroy vesicles.
Exocytosis is used for the following purposes:
- Release enzymes, hormones, proteins and glucose for use in other parts of the body
- Neurotransmitters (in the case of neurons)
- Communicate defense measures against a disease
- Eject cell debris
Endocytosis is used for the following purposes:
- Receive nutrients
- Pathogen Entry
- Migration and cell adhesion
- Signal receivers
Summary:
- Endocytosis attracts molecules into a cell, while exocytosis removes molecules from a cell.
- Both processes use vesicles for molecular transport.
- Endocytosis creates vesicles, while exocytosis can destroy them.
- The main function of endocytosis is to obtain nutrients and the main function of exocytosis is to expel waste.
You May Also Interested:
