What is Difference between central and peripheral nervous system?
The difference between central and peripheral nervous systems is that The nervous system is a complex system made up of nerves and cells that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord and other parts of the body. It controls and integrates the different bodily functions and maintains the stability and constancy of the internal variables of our body. 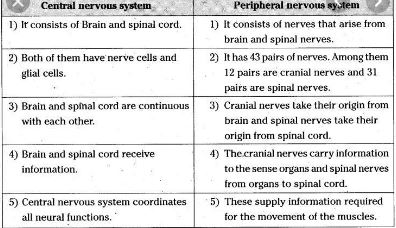
The nervous system is responsible for three basic functions of our body: sensory, integrative and motor function. The nervous system is divided mainly into two: the central and peripheral nervous systems.
The central nervous system controls voluntary functions such as walking, laughing, reading, etc. While the peripheral nervous system is responsible for involuntary actions such as blinking, heartbeat, digestion, etc. In this article of Psychology-Online, we tell you the differences between the peripheral and central nervous systems.
The central nervous system (CNS): function
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of two main parts: the brain and spinal cord.
- The brain plays a central role in controlling most bodily functions, including movements, sensations, thoughts, speech, memory, etc. Some reflex movements can occur through the spinal cord without the involvement of brain structures. The brain is made up of four main parts: brainstem, brain, cerebellum, and diencephalon. There are two types of substances in the brain, gray and white. The gray matter (cell bodies of neurons and neuroglia) receives and stores impulses. And the white substance, formed by axons, carries impulses to and from the gray substance.
- The spinal cord is connected to a section of the brain called the brainstem and is inside the spine. It is composed of a series of 31 segments. A pair of cranial nerves leave each segment. The motor and sensory nerves are found in the spinal cord that transmits signals (messages back and forth between the brain and peripheral nerves).
The peripheral nervous system (SNP) and its parts
The peripheral nervous system is the division of the nervous system that contains all the nerves outside the central nervous system (CNS). Its main function is to connect the CNS with the organs, limbs, and skin. These nerves extend from the central nervous system to the most peripheral areas of the body. It allows the brain and spinal cord to receive and send information to other areas of the body, which makes us react to the stimuli of our environment. The nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system are actually axons or are axons of neuronal cells.
The peripheral nervous system is divided into two parts autonomic and somatic nervous system:
Difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous system
The somatic nervous system is responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system. It is responsible for transmitting sensory information and voluntary movement. This system contains two main types of neurons:
- Sensory (afferent) that carry information from the nerves to the CNS. It is these neurons that allow us to receive sensory information and send it to the brain and spinal cord.
- Motor: that transport information from the brain and spinal cord to muscle fibers throughout the body. These motor neurons allow us to perform physical actions in response to stimuli in the environment.
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as blood flow, heartbeat, digestion, and breathing. So it is generally this part of the system that controls aspects of the body that are not under voluntary control. This system allows these functions to be carried out without thinking that they occur consciously.
In turn, it is divided into two, the sympathetic system (prepares the body to spend energy and face possible threats to the environment) and parasympathetic (helps maintain normal body functions and conserve physical resources, once the Threat this system will allow the body to return to a normal state). Discover in the following article the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system: differences and functions.
You May Also Like:
