Microscope and its types
Different types of microscopes, Explore the top four and more
What is microscope and microscopy terms
- The use of a microscope is called microscopy.
- The first compound microscope was invented by Zacharias Janssen, in Holland in 1559 which have magnification ranged from 3X to 9X.
- Two Important terms used in microscopy are magnification and resolving power.
- Magnification: It is the increase in the apparent size of an object.
- Resolving power or resolution: It is the measure of the clarity of an image. It is the minimum distance at which two objects can be seen as separate objects.
- The human eye can differentiate between two points which are at least 0.1mm apart. This is called the resolution of the human eye.
- Magnification and resolution can be increased with the help of lenses.
4 different types of microscopes and their uses
There are several different types of microscopes used in optical microscopy, and the four most common types are
- Compound microscopes
- Stereo microscopes
- Digital microscopes
- Pocket or handheld microscopes.
Some types are best suited for biological applications, others are specific for classroom use or personal hobbies.
Outside the Light Microscope, There are exciting developments with electron microscopes and scanning.probe microscopy.
The following is a brief introduction to the different types available.
A- Light Microscope / Compound Light microscope (LM)
The light microscope is made up of two glass lenses, a mirror, and a stage.
Functioning
- The light microscope works by passing visible light through the specimen.
- One lens produces an enlarged image of the specimen and second lens magnifies that image.
- Image is then projected into the viewer’s eye or photographic film.
- A photograph taken by a microscope is called micrograph.
- Resolving power of Light microscope is 2um.
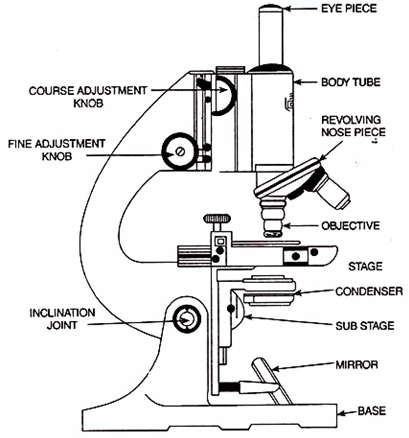
compound light microscope
Common binocular (with two eyepieces), a Compound light microscope usually combines the power of the lenses and the light to magnify the subject being examined.
The lens itself usually allows 10x or 15x magnification and when combined with three or four objective lenses, which can be rotated in the field of view, produces a maximum

magnification of up to a maximum of 1000X.
The compound light microscope is popular among botanists to study plant cells, in biology to see bacteria and parasites as well as a variety of human/animal cells.
It is a useful microscope in forensic laboratories to identify drug structures.
As its simple models are readily available and inexpensive so compound light microscopes are one of the most common types of microscopes, often found in science and biology labs.
Many microscopic imaging techniques benefit scientists and researchers who use a compound microscope and explore specimens in detail.
B- Stereo microscope
The stereoscopic microscope, also known as the dissection microscope, has two optical paths at slightly different angles allowing the three-dimensional image to be displayed

under the lenses.
Stereoscopic microscopes magnify specimens at relatively low power, typically between 10x and 200x, generally less than 100x.
With this type of microscope, you can choose to buy a fixed set or zoom from a relatively inexpensive manufacturer.
The uses of this type of microscope include looking at surfaces, microscopic surgery and clock making, as well as building and inspecting circuit boards.
Stereo microscopes allow students to monitor plant photosynthesis at work.
C- Digital microscope
Stepping into the 21st century using a digital microscope and exploring the world of amazing detail.
The digital microscope, invented in Japan in 1986, uses the computer power to display objects invisible to the naked eye.
Among the different types of microscopes, this type can be found with or without eyepiece.
It is connected to a computer via a USB cable, much like connecting a printer or mouse. The computer program allows the screen to display the enlarged sample. You can record moving pictures or capture individual images in your computer’s memory.
The digital microscopes feature the ability to send images by e-mail, as well as to watch animations comfortably for long periods of time.
The popularity of digital microscopy in schools has increased among students and hobbyists.
D- Pocket Microscope

When examining the different types of microscopes available in the market, the pocket microscope is small but its capabilities are impressive.
This is a device that is a great gift for your child or for your students. It is used by scientists for hand-imaging of a variety of samples/objects in the field or in the laboratory.
It is small, durable and portable with a magnification ranging from 25x to 100x. There are many different models available.
E- USB PC Microscope
Although they are not well suited to the same scientific applications as other optical microscopes, a computer’s microscope can be used, among different types of microscopes, for almost any specimen and does not require any sample preparation.
It uses basically a macro lens to scan images displayed on a computer screen connected to its USB port.
However, magnification is restricted and can not be compared to your standard compound light microscope up to 200X with a relatively small field depth.
It is Ideal for hobbies and kids and is inexpensive at a purchase price of less than $ 200.
F- Electron microscope (EM)
Among the different types of microscopes, the electron microscopy (EM) is a powerful microscope available and used today, which allows scientists to see a sample the size of a

nanometer. It is composed of a vacuum chamber, electromagnetic lenses, screen or photographic film and source of an electron beam.
Functioning:
- In EM, object and lens are placed in a vacuum chamber and beam of an electron is passed through the object.
- Electrons pass through or reflected from object make an image.
- Electromagnetic lenses enlarge an image and focus it on screen or photographic film.
- EM has magnification power up to 250000X and resolution power 0.2nm.
- EM can detect atoms, molecules and organelles.
Types of Electron microscope
- The Transmission electron microscope (TEM) is the first type of Electron Microscope which is capable of producing even 1 nm sized images. n TEM electrons are passed through the specimen to see the internal structure.TEM is the best-suited choice for nanotechnology, semiconductor analysis, and production.

scanning electron microscope image of arms of octopus eledone larva - The second type of electron microscope is a scanning electron microscope (SEM) that is about 10 times less than TEMs. In SEM electron is reflected from metal coated surfaces to see the structure of cell surfaces. SEM produces sharp, high-resolution, black and white three-dimensional images.
Scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes have diversified range of practical applications in areas such as biology, chemistry, gemmology, metals, and industry, as well as information on topography, composition, morphology and crystallographic data of specimens.
G- Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
Among the different types of microscopes and microscopy techniques, Scanning Probe Microscopy is used today in the academic and industrial environments of those sectors, which include physics, biology, and chemistry. These tools are used in research and development as standard analytical tools.

Images are greatly enlarged and are observed in 3D shapes in real time. SPMs use a precise probe to scan the sample surface, eliminating the constraints in the electron and light microscope.
H- Acoustic microscope
The “acoustic microscope” focus less on resolution and more to detect errors, cracks or errors of the samples during the manufacturing process.

By using high ultrasound, this type of microscope is the easiest tool available for intracavity imaging. It is a microscope that is underused because of the fact that it is less known for its capabilities.
Scanning acoustic microscopy, or SAM, is the latest type of acoustic microscope available for today’s scientists. They can use it to display a sample’s internal structure without staining or causing any damage by point focus technology, which relies on an optical beam to scan the sample and penetrate it even within the water.
