What is Difference Between Endosmosis And Exosmosis?
Difference Between Endosmosis And Exosmosis is that Endosmosis and exosmosis are both types of osmosis, but endosmosis is the movement of water into a cell, while exosmosis is the movement of water out of a cell. Endosmosis occurs when the inside of a cell is hypertonic and has low water potential, while exosmosis occurs when the inside of a cell is hypotonic and has a high water potential.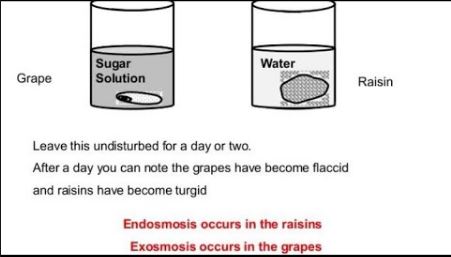
What is endosmosis?
Definition of Endosmosis:
Endosmosis is the movement of a solvent (usually water) through a semipermeable membrane from a region outside a cell where there is a high solvent content, under solute, towards a cell where it is low solvent, high solute. Endosmosis is a type of osmosis. Osmosis is the passive diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane along a concentration gradient from where there is a high concentration of water to where there is a low concentration of water.
Tonicity and water potential in Endosmosis:
The inside of the cell is hypertonic, that is, it has a higher concentration of solute than the outside of the cell. The exterior of the cell is, therefore, hypotonic has a lower solute concentration in relation to the interior of the cell. Water potential is the tendency for water to move from where there is a high water potential to low water potential and where there is more solute present, there will be a lower water potential. Water, therefore, moves endosmosis to a hypertonic cell of low water potential from a hypotonic external environment of high water potential.
Effects of Endosmosis:
Endosmosis increases the pressure of a cell’s turgidity since the water that enters causes the cytoplasm to push against the cell membrane and the cell wall (if it is a plant cell), which causes the cell to become turgid. Endosmosis can cause the cell to swell considerably as more water enters. If a cell is surrounded by pure water, too much water may enter to the point that the cell swells so much that it explodes, which occurs more frequently in animal cells than in plant cells, since cells have a cellular wall..
Animal example for endosmosis:
A freshwater fish may experience changes in ion concentrations in the water in which it lives. The cells of a freshwater fish can sometimes be hypertonic compared to the external environment. This means that the fish has to osmoregulate and compensate for endosmosis by excreting large amounts of diluted urine.
Human meaning in endosmosis:
Endosmosis is important as it is a process that is needed to keep us alive, but at the same time, if endosmosis occurs too quickly, a person’s cells can be destroyed and their survival may be compromised. For example, people who drink too much water too quickly may end up with water poisoning or hyponatremia (low sodium).
What is exosmosis?
Definition of exosmosis:
Exosmosis is the movement of a solvent (usually water) through a semipermeable membrane from inside a cell where there is a high solvent, under solute out of a cell where it is low solvent, high solute. Exosmosis is also a type of osmosis.
Tonicity and water potential:
The inside of the cell is hypotonic towards the outside of the cell. The exterior of the cell is, therefore, hypertonic within the cell. In this way, water moves from the high, hypotonic water potential within the cell to the low water potential, hypertonic external environment.
Effects of exosmosis:
When exosmosis occurs, water leaves the cell to the external environment. As this happens, the cytoplasm contracts because of the loss of water. If exosmosis occurs too quickly and too much water is lost, the cytoplasm will be reduced (plasmolysis). If the cytoplasm shrinks too much, it could cause the cell to contract (more commonly occurs in animal cells than in plant cells).
Animal example for exosmosis:
A saltwater fish may experience changes in ion concentrations in the water in which it lives. The cells of a saltwater fish can be hypotonic compared to the external environment. This means that fish have to osmoregulate and compensate for exosmosis by drinking seawater and producing a small amount of urine.
The human meaning of exosmosis:
Too much exosmosis can lead to dehydration since water is lost from our cells. Severe dehydration can lead to death.
Difference between Endosmosis and Exosmosis.
-
Solvent movement
In endosmosis, the solvent moves into a cell while in exosmosis the solvent moves out of the cell.
-
Solute concentration
In endosmosis, the highest concentration of solute is within the cell, while in exosmosis the highest concentration of solute is outside the cell.
-
Solvent concentration
In endosmosis, the highest concentration of solvent is outside the cell, while in exosmosis, the highest concentration of solvent is within the cell.
-
Water potential
The water potential in endosmosis is higher outside the cell than inside, while the water potential in exosmosis is higher inside the cell than outside the cell.
-
Effects
In endosmosis, the cell becomes inflamed and becomes turgid, and may burst (occurs more frequently in animal cells).
In exosmosis, the cytoplasm shrinks and the cell can shrink (occurs more frequently in animal cells).
-
Plant example
Water moves by endosmosis to the hair cells of the root from the ground, while water leaves the hair cells of the root by exosmosis to the cortex.
-
Animal example
Freshwater fish undergo an endosmosis, while saltwater fish undergo an exosmosis.
-
Human meaning
Humans can suffer from water poisoning if there is too much endosmosis, while they can suffer from dehydration if there is too much exosmosis.
Comparative table of the difference between Endosmosis and Exosmosis
Summary of Endosmosis vs. Exosmosis
- Endosmosis and exosmosis are both types of osmosis, but endosmosis is the movement of water into a cell, while exosmosis is the movement of water out of a cell.
- Endosmosis occurs when the inside of a cell is hypertonic and has low water potential, while exosmosis occurs when the inside of a cell is hypotonic and has high water potential.
- Too much endosmosis or exosmosis can be dangerous.
- Endosmosis and exosmosis must be carefully regulated so that cells remain alive.
You May Also Interested:
