What is Difference Between Biotic And Abiotic?
Abiotic factors refer to physical and chemical non-living elements in the ecosystem. Abiotic resources are generally obtained from the lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere. Examples of abiotic factors are water, air, soil, sunlight, and minerals. Biotic factors are organisms that are living or that lived in the ecosystem. These are obtained from the biosphere and are capable of reproduction. Examples of biotic factors are animals, birds, plants, fungi, and other similar organisms.

Biotic components are living organisms in an ecosystem. The abiotic factor is a living organism that affects another organism in its ecosystem. Examples include plants and animals that the body consumes as food and the animals that consume the body. The following video covers the biotic and abiotic factors that influence most ecosystems, and introduces the key vocabulary relevant to ecology: This is a good SlideShare presentation that covers the definition and examples of biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem:
The scope of biotic and abiotic factors extends across the entire biosphere, or the global sum of all ecosystems. Such factors may have relevance for an individual within a species, its community or an entire population. For example, the disease is an abiotic factor that affects the survival of an individual and his community. Temperature is an abiotic factor with the same relevance.
Some factors are more relevant to an entire ecosystem. Abiotic and biotic factors combine to create a system or, more precisely, an ecosystem, that is, a community of living and non-living things considered as a unit. In this case, the abiotic factors include the soil and water pH, types of nutrients available and even the length of the day. Biotic factors such as the presence of autotrophic organisms or self-feeding organisms, such as plants, and the diversity of consumers also affect an entire ecosystem.
Influencing factors
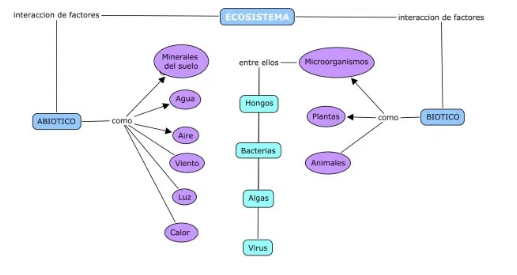
Abiotic factors affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce. Abiotic limiting factors restrict population growth. They help determine the type and number of organisms capable of existing within an environment. Biotic factors are things that directly or indirectly affect organisms within a living environment. This includes the organisms themselves, other organisms, the interactions between living organisms and even their residues. Other biotic factors include parasitism, disease, and predation (the act of eating one animal from another).
Difference Between Biotic And Abiotic
The importance of biotic and abiotic factors comes in their interaction with others. For a community or an ecosystem to survive, the correct interactions must be in place. A simple example would be of abiotic interaction in plants. Water, sunlight and carbon dioxide are necessary for plants to grow. The biotic interaction is that plants use water, sunlight and carbon dioxide to create their own food through a process called photosynthesis.
On a larger scale, abiotic interactions refer to patterns such as weather and seasonality. Factors such as temperature, humidity and the presence or absence of stations affect the ecosystem. For example, some ecosystems experience cold winters with a lot of snow. An animal, such as a fox within this ecosystem, adapts to these abiotic factors by the growth of a thick, white layer in the winter.
Decomposers such as bacteria and fungi are examples of biotic interactions on such a scale. Decomposers work by breaking dead organisms. This process returns the basic components of organisms to the soil, which allows them to be reused within that ecosystem.
You May Also Interested:
