What is Difference between Mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis and meiosis are two different forms of cell division in eukaryotic cells, those that have a nucleus.
During the cell cycle, the eukaryotic cell undergoes a series of changes that lead to the formation of new cells. Depending on the type of cell, it can be divided by mitosis or meiosis.
For example, in organisms that have sexual reproduction, germ cells divide by meiosis to give rise to sex cells or gametes. On the other hand, somatic cells only divide through mitosis.
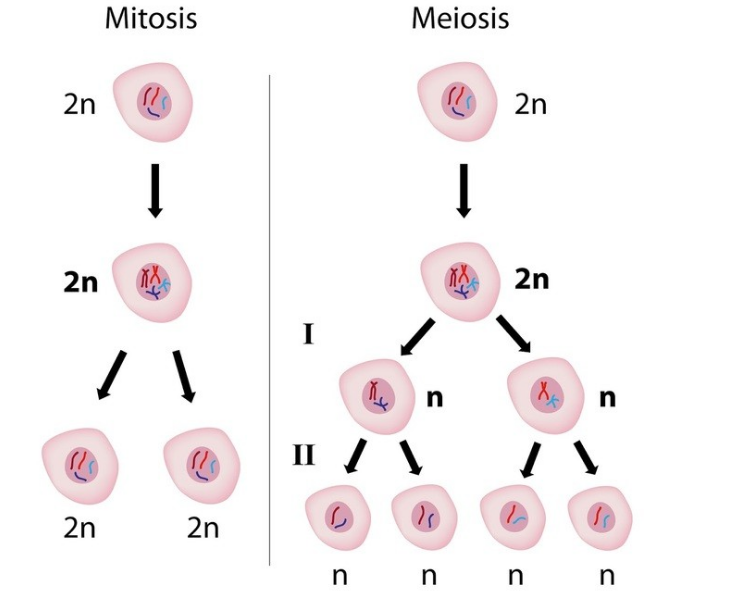
| Mitosis | Meiosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nuclear division process in which two nuclei with the same number of chromosomes of the cell of origin are generated. | The nuclear division process originates four cells with half the number of chromosomes in the cell of origin. |
| Stages or phases |
| Meiosis I:
Meiosis II:
|
| Number of nuclear divisions | one | 2 |
| Number of genetic duplications | one | one |
| Cross-linking and chromosomal recombination | Absent. | Present in prophase I and metaphase I. |
| Outcome | Two daughter cells with the same amount of genetic material. | Four cells with half the genetic material. |
| Example | Dermis cells proliferate to renew skin cells. | Germ cells located in the gonads produce gametes. |
Mitosis
Mitosis is a process of cell division that occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, after duplication of genetic material at the interface. This process is present in both unicellular and multicellular beings. It is also known as karyokinesis.
In mitosis, a diploid cell gives rise to two diploid cells with the same genetic information.
Phases of mitosis
Mitosis is a continuous process where four successive phases can be identified:
- Prophase: the genetic material begins to condense and form long, thin strands. The mitotic spindle is formed.
- Metaphase: the disappearance of the nuclear envelope or chariot and location of chromosomes in the cellular equator.
- Anaphase: the chromosomes migrate to the poles of the cell.
- Telophase: at each pole of the cell the nuclear envelope begins to reorganize surrounding the chromosomes that are already decompacting.
Mitosis is followed by the process of cytokinesis or cytokinesis, that is, the division of the cytoplasm to originate two daughter cells.
you can see the formation of the mitotic spindle, which is that structure as a starfish with a yellow center and red tentacles. Chromosomes look like plump worms, which are being dragged by the spindles to opposite ends of the cell.
Importance of mitosis
Mitosis occurs in undifferentiated somatic cells and pluripotential cells. Its importance is that it is essential for the following cellular processes:
- Development: from the zygote, which is the first cell of a multicellular individual, the millions of different cells that constitute a superior organism are generated.
- Growth: allows an increase in the number of cells in organisms, promoting their growth.
- Tissue repair and renewal: new cells are regenerated by mitosis to replace cells that die or are lost.
Meiosis
Meiosis is the process of cell division of a diploid cell (2n) to give rise to four haploid cells (1n). The result is the gametes or sex cells: the sperm in the male and the ovules in the females of most species.
The general process of meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions, without duplication of the genetic material in the intermediate step. In addition, cross-linking and chromosomal recombination occurs, so the four resulting cells do not necessarily carry the same genetic information.
Phases of meiosis
Since meiosis occurs after two nuclear divisions, known as meiosis I and meiosis II, the phases receive the same name as the stages of mitosis followed by the number of the period in which they occur:
MEIOSIS I
- Prophase I: homologous chromosomes mate and exchange genetic material by crosslinking.
- Metaphase I: Chromosomes are located in the equator of the cell randomly.
- Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes are separated and directed to the cell’s poles.
- Telophase I: The chromosomes that are already at the poles begin to disorganize and be surrounded by the nuclear envelope.
When this first period of cell division ends, two diploid cells with the same amount of genetic material are obtained.
MEIOSIS II
Daughter cells of the period I enter a short interface II, where the chromosomes are disorganized and there is no genetic duplication.
- Prophase II: Chromatin condenses again and the nuclear envelope disappears.
- Metaphase II: The chromosomes formed by two chromatids are located in the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase II: sister chromatids separate and are carried to the cell’s poles.
- Telophase II: Chromosomes now with a single chromatid are found at the poles and the nuclear envelope around them begins to reorganize.
At the end of this second period of nuclear division, the result is four haploid cells, each with half the genetic material.
You May Also Interested:
Recent Posts
Types of Cells
Living things are made up of cells, the basic unit of life. There are many types…
What is the Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
The difference between HIV and AIDS is that AIDS is the disease caused by HIV infection. You…
What is Difference between Antisepsis and asepsis?
The Difference between Antisepsis and asepsis is that The antisepsis is the procedure performed to reduce…
Virus vs bacteria
Virus vs bacteria: The difference between viruses and bacteria lies in the fact that the virus…
What is Difference between Arches and bacteria?
Major Difference between Arches and bacteria is that The archaea and bacteria are prokaryotes, unicellular living whose genetic material…
What is The Difference Between DNA and RNA?
The difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is…


