25 Branches Of Biology A to Z List With Definitions Meanings & Examples
The branches of biology
THE MAIN BRANCHES OF BIOLOGY
Main divisions and Branches of biology
Biologists study the structure, composition, growth, metabolism origin, geographical distribution, and evolution of living organisms. Three main divisions of biology are Microbiology, Botany and zoology under the umbrella of which many branches and sub-branches come. Here in this topic, we will cover definitions and examples of main branches such as morphology, anatomy, genetics, embryology, biotechnology, pharmacology, parasitology, physiology, etc. Biology overlaps with physics, chemistry, math, economics, and forms biophysics, biochemistry, biomathematics, bioeconomics respectively. These interdisciplinary branches will also be discussed here.
The topic is still continued………..
Stay with us to learn about 25 main branches and divisions of biological science which are famous and encountered by us, mostly in our daily life.
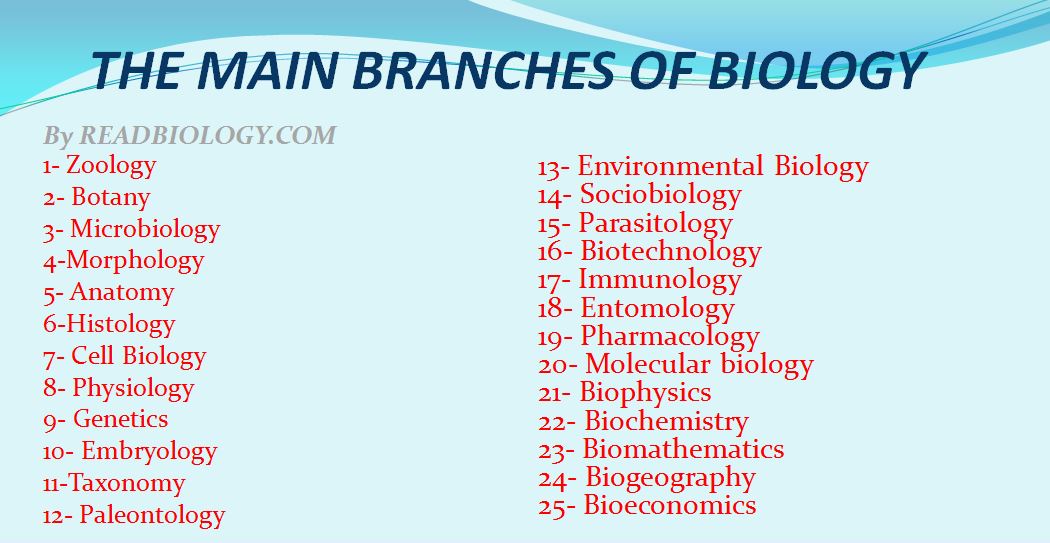
Here is the list of 25 main branches of Biology
1- Zoology
2- Botany
3- Microbiology
4-Morphology
5- Anatomy
6-Histology
7- Cell Biology
8- Physiology
9- Genetics
10- Embryology
11-Taxonomy
12- Paleontology
13- Environmental Biology
14- Sociobiology
15- Parasitology
16- Biotechnology
17- Immunology
18- Entomology
19- Pharmacology
20- Molecular biology
21- Biophysics
22- Biochemistry
23- Biomathematics
24- Biogeography
25- Bioeconomics
Divisions of biology
The umbrella of biology mainly covers three vast fields which are called divisions of biological sciences. These are defined as follows.
1- ZOOLOGY (/zuˈɒlədʒi, zoʊ-/) This division of biology deals with the study of animals. For Example Wild animals, farm animals, pets, etc
2- BOTANY (/BAWT-(ə)-nee/) This division of biology deals with the study of plants.
For Example, The study of your favorite plants i.e. rose, maple tree, onion, etc. Plants may be herbs, shrubs, trees, creepers, flowering, non-flowering, vegetable plants, fruits plants, etc.
3- MICROBIOLOGY (/MIKE-rō-bī-AWL-ə-jee/) This division of biology deals with the study of microorganisms such as bacteria, microscopic fungus, algae, etc.
Main branches of biology
1- Morphology: (/mɔːˈfɒlədʒi/) This branch deals with the study of form, size, shape, and structure of living organisms. e.g. skin color, height, the shape of limbs, etc.
2- Anatomy (/ə-NAT-ə-mee/) The study of internal structures of living organisms by dissection is called anatomy e.g. internal structure of the kidney.
3- Histology (/hist-TAWL-ə-jee/) The microscopic study of structural tissues of organisms is called histology e.g. study of muscles, adipose, connective tissue, etc.
4- Cell biology: The study of the structures and functions of cells and cell organelles is called cell biology. This branch also deals with the study of cell division. e.g. muscle cell.
5- Physiology (/fizz-ee-AWL-ə-jee/) This branch deals with the study of the functions of different parts of living organisms e.g. working of muscles.
6- Genetics (/dʒəˈnɛtɪks/) The study of genes and their roles in inheritance is called genetics. Inheritance means the transmission of characters from one generation to the other e.g. Blood group genetics.
7- Embryology (/em-bree-AWL-ə-jee/) It is the study of the development of an embryo to new individual e.g. study of various stages of chick development.
8- Taxonomy (/takˈsɒnəmi/) It is the study of the naming and classification of organisms into groups and subgroups. e.g. identification of the taxonomic position of a newly discovered animal species in an area.
9- Paleontology (/pæl.i.ɒnˈtɒl.ə.dʒi/) It is the study of fossils, which are the remains of extinct organisms e.g. estimating the age of the dinosaur’s skeleton.
10- Environmental biology: It deals with the study of the interactions between organisms and their environment. For Example, the effect of pollution on human health or human activities increases pollution on the planet.
11- Socio-biology: This branch deals with the study of social behavior of the animals that make societies.For Example: protective behavior of mothers to their offspring, killing of cubs by a male lion to reduce competition in their offspring.
12- parasitology (/pare-ə-sə-TAWL-ə-jee/) This branch deals with the study of parasites e.g. study of mosquito, bacteria. worms harming the bodies of animals are all parasites. Plants also have other parasitic plants i.e. Cuscuta.
13- Biotechnology (/baɪ.əʊ.tekˈnɒl.ə.dʒi/) It deals with the practical application of living organisms to make substances for the welfare of mankind. Its best example is using bacteria for producing human hormones such as Insulin, growth hormones, etc.
14- Immunology (/IM-yə-NAWL-ə-jee/) It is the study of the immune system of animals, which defends the body against invading microbes. For Example: How White blood cells engulf foreign particles is actually an immunity study.
15- Entomology (/en.təˈmɒl.ə.dʒi/) It is the study of insects. For Example: If someone wounder why ants form Que and how honeybees search for insects, all this comes in Entomology.
16- Pharmacology (/fɑː.məˈkɒl.ə.dʒi/) It is the study of drugs (medicines) and their effects on the systems of the human body. For Example: If a doctor is studying the effects of cinchona bark extract on malaria patients, he is studying pharmacology.
17- Molecular biology (biochemistry /ˌbaɪ.əʊˈkem.ɪ.stri/ ) It deals with the study of the molecules of life. For Example Study of the role of water, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids molecules in maintaining life.
Interdisciplinary branches of biology
Well: “Biology is not as simple”
It also makes links with the other disciplines of science, thus giving birth to new biology disciplines or branches. This enables us to understand biology in a better way in light of the principles of the other sciences. Branches that are formed due to interlinking of biology with other fields are following.
1- Biophysics: It deals with the study of the principles of physics, which are applicable to biological phenomena. For example limbs of animals work on the principle of the lever in physics.
2- Biochemistry: It deals with the study of the chemistry of different compounds and processes occurring in living organisms. For Example Study of photosynthesis and respiration.
3- Biomathematics / Biometry: It deals with the study of biological processes using mathematical techniques and tools. For Example: “To analyze the data of the animal’s population”.
4- Biogeography: It deals with the study of the occurrence and distribution of different species of living organisms in different geographical regions of the world. For Example, Acacia is found in the desert.
5- Bioeconomics: It deals with the study of organisms from an economical point of view. For Example the cost or profit value of the yield of wheat.
Related links
- Click here to read more about the definition meaning and scope of ZOOLOGY
- Click here to read more about the definition meaning and scope of MICROBIOLOGY
- Click here to read more about the definition meaning and scope of CELL BIOLOGY
- Click here to read more about the definition meaning and scope of BIOCHEMISTRY
- Click here to read more about the definition meaning and scope of BIOTECHNOLOGY
- 25 branches of biology and their definitions
- 25 Branches Of Biology A to Z List With Definitions Meanings & Examples
- “Perfect list” of 25 main branches of biology with definitions and examples
- Three divisions of biology are microbiology, botany, and zoology. Main branches of biology are morphology, anatomy, genetics, paleontology,
Recent Posts
Types of Cells
Living things are made up of cells, the basic unit of life. There are many types…
What is the Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
The difference between HIV and AIDS is that AIDS is the disease caused by HIV infection. You…
What is Difference between Antisepsis and asepsis?
The Difference between Antisepsis and asepsis is that The antisepsis is the procedure performed to reduce…
Virus vs bacteria
Virus vs bacteria: The difference between viruses and bacteria lies in the fact that the virus…
What is Difference between Arches and bacteria?
Major Difference between Arches and bacteria is that The archaea and bacteria are prokaryotes, unicellular living whose genetic material…
What is The Difference Between DNA and RNA?
The difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is…