Functions of Endocrine System
The Endocrine System is a set of organs that generate and secrete hormones (substances that act as chemical messengers), these reach different parts of the human body to regulate, control and coordinate the functions of various organs.
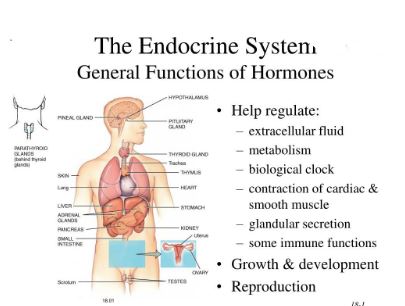
Functions of the Human Endocrine System
The function of the Endocrine System is the internal communication of the human organism, unlike the Nervous System (the other internal communication system) that communicates thanks to the nerve impulses in the nerves that function as a series of cables distributed by the body, the Endocrine communicates by sending hormones through the bloodstream and can reach areas of the human body that the Nervous System does not reach .
That communication also varies from one system to another, since the actions of the Nervous System are faster and of short duration, the actions of the Endocrine System are slower and of long duration.
Let’s look at these schematized differences:
| FEATURES | ENDOCRINE SYSTEM | NERVOUS SYSTEM |
| FUNCTION | Internal communication | Internal communication |
| DELIVERY COURIER | Hormone | Nerve impulse |
| CHANNEL | Bloodstream | Nerves |
| TYPE OF COMMUNICATION | Fast and short | Slow and prolonged |
Organs of the Human Endocrine System
Endocrine means “internal secretion” by what the endocrine organs are called internal secretion glands, and the Endocrine System is the Internal Secretion Gland System.
There are exocrine glands (external secretion) belonging to the Exocrine System, which create enzymes and use ducts to transport the secretion to the body or organ surface, and the endocrine glands that secrete hormones and use the bloodstream to reach the fluid interstitial cells.
The glands of the endocrine system can also be classified according to the place of action and the specific receptors prepared to capture them:
- AUTOCRINE HORMONES: they act in the cell where it is created, for example, the hormone Interleukin that sends signals to the cell to increase its immune capacity.
- PARACRINE HORMONES: they act in the regional area near where they have been produced, such as hormones created in the Hypothalamus that act in the Pituitary that is very close.
- ENDOCRINE OR CLASSIC HORMONES: they act at a distance, like the hormones that are created in the Pituitary and act in the gonads.
Glands of the Endocrine System
To understand how the endocrine glands work we will see what they are, what type of hormones each one secretes and in which organs of the human body they act.
Pineal gland
The pineal gland secretes melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxy-tryptamine), a hormone that regulates sleep and circadian rhythms.
Its size is 5 to 8mm, like a grain of rice, this gland is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by luminosity through the photosensitive cells of the retina, hence adapting the biological rhythm of the body at 24 hours day.
Pituitary gland
Gland controlled by the Hypothalamus, so that 2 systems overlap: the Nervous System and the Endocrine System.
The hypothalamus is the size of an almond and the pituitary gland of a pear-shaped pea, the first receive nerve impulses and channels them to the second communicating with its anterior part or lobe, the adenohypophysis, and its posterior part or lobe, the neurohypophysis.
The hormones that arrive from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland are paracrine (regional) and we will name them as they stimulate the secretion of other hormones in the anterior or posterior pituitary gland.
We will start with the adenohypophysis :
- HRT: a thyrotropin-releasing hormone that stimulates the secretion of TSH (a hormone that stimulates the thyroid) and PRL (prolactin, a hormone that stimulates breastfeeding and autoimmunity) in the adenohypophysis.
- CRH: a corticotropin-releasing hormone that induces the release of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic, a hormone that increases cortisol and corticosterone levels in the blood) in the adenohypophysis.
- GHRH: Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GH) in the adenohypophysis.
- GnRH: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone that induces the release of LH (lutropin, a hormone that triggers ovulation and testosterone production) and FSH (a follicle-stimulating hormone that helps generate ovarian follicles for the ovary and sperm maturation in the testicles ) in the adenohypophysis.
- GHIH: somatostatin, inhibited GH hormone or growth hormone.
- PIF: prolactin inhibitor hormone or PRL.
GnRH stimulates the secretion of LH and FSH.
HRT stimulates the secretion of TSH and PRL.
CRH stimulates ACTH secretion.
GHRH stimulates the secretion of GH.
On the other hand, we have hormones that are created in the hypothalamus and stored in the neurohypophysis and are endocrine because they act at a distance:
- ADH: vasopressin, an antidiuretic hormone that retains water in the kidney.
- Oxytocin: a hormone that stimulates the contraction of the uterus during childbirth and the injection of breast milk.
Thyroid gland
The thyroids are in the trachea and secrete the hormones T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine) that regulate metabolism, and the calcitonin that regulates calcium in bones and cells.
Thymus
The thymus generates the thymosin hormone that is involved in the development of T cells that are immunological.
Kidney glands
They are above the kidneys and are divided into:
- SR cortex: the external part that secretes cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens, related to stress reaction, inflammation, metabolic and renal functions.
- Medulla SR: the internal part where the catecholamine hormones that secrete adrenaline and norepinephrine are related to stressful and survival responses of the body.
Pancreas
It has exocrine and endocrine function, the latter is responsible for the metabolism of blood glucose. When the pancreas secretes insulin decreases the passage of glucose to the cells and when it secretes glucagon increases it.
Gonads
The gonads are divided according to whether they are female or male and secrete the following hormones:
- FEMALE OR OVARIAN GONADES: estrogens and progesterone that regulate female sexual functions.
- MALE GONADES or TESTICLES: which secrete testosterone related to male sexual functions.
An alternative classification of the Endocrine Glands
Once the endocrine glands are known, we can see an alternative classification based on their chemical structure: Functions Endocrine System
- PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES: they are the majority of hormones, they are of variable size according to the number of amino acids they contain (+100 amino acids = Protein / -100 = Peptide), they are synthesized in the Rugged Endoplasmic Reticulum and they are water-soluble but they are not easily pierced cell tissues.
- STEROIDS: they are synthesized from cholesterol, they are fat-soluble which makes them easy to penetrate the cell membrane and are hormones such as cortisol, testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone.
- DERIVATIVES OF THYROXINE: two hormones that are synthesized in the thyroid creating the hormones T3 and t4 and in the adrenal medulla, secreting the catecholamine hormones. Functions Endocrine System
You May Also Like:
Recent Posts
Types of Cells
Living things are made up of cells, the basic unit of life. There are many types…
What is the Difference Between HIV and AIDS?
The difference between HIV and AIDS is that AIDS is the disease caused by HIV infection. You…
What is Difference between Antisepsis and asepsis?
The Difference between Antisepsis and asepsis is that The antisepsis is the procedure performed to reduce…
Virus vs bacteria
Virus vs bacteria: The difference between viruses and bacteria lies in the fact that the virus…
What is Difference between Arches and bacteria?
Major Difference between Arches and bacteria is that The archaea and bacteria are prokaryotes, unicellular living whose genetic material…
What is The Difference Between DNA and RNA?
The difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is…
